Unmasking the Land: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Australian Aboriginal Reservations
Unmasking the Land: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Australian Aboriginal Reservations

Australia’s landscape is a tapestry woven with the stories and traditions of its First Peoples, the Aboriginal Australians. For millennia, they have lived in harmony with the land, their cultures deeply entwined with the natural world. However, the colonial history of Australia has led to a complex and often misunderstood reality: the establishment of reserves, areas designated for Aboriginal people.
This article delves into the intricacies of Australian Aboriginal reservations, exploring their historical context, current realities, and the ongoing fight for self-determination. We’ll examine the map of these reservations, highlighting their geographical distribution and the diverse communities they represent.
Related Articles: Unmasking the Land: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Australian Aboriginal Reservations
- Beyond The Familiar: 9 Animal Names With Indigenous Origins
- A Tapestry Of Connection: How Aboriginal Peoples Used The Land
- Unraveling The Tapestry Of Land: A Journey Through Indigenous Maps And Symbols Of Australia
- The Animal Kingdom In Aboriginal Art: A Journey Through Symbolism And Storytelling
- Weaving Ancient Wisdom Into Modern Vows: Embracing Indigenous Ceremony Leaders In Australian Weddings
Understanding the Terminology: Reservations, Communities, and Land Rights
The term "reservation" often carries a loaded history, conjuring images of confinement and limitations. In the Australian context, it’s crucial to understand the nuances of this term. While "reservation" is still commonly used, it’s important to acknowledge the evolving language surrounding Aboriginal land rights.
"Community" is often preferred as it emphasizes the sense of belonging and self-governance within these areas. "Land rights" refers to the legal recognition of Aboriginal ownership and control over their traditional lands.
A History of Dispossession and Resistance
The arrival of European settlers in the 18th century marked a turning point in the history of Aboriginal Australia. The concept of land ownership, alien to Aboriginal culture, led to a systematic dispossession of their ancestral lands. The British Crown, through various acts and policies, asserted ownership, pushing Aboriginal people into designated areas known as "reservations."
These reservations were often seen as a means of control, segregating Aboriginal people from the wider society and limiting their access to resources and opportunities. The policies of assimilation, aiming to absorb Aboriginal people into mainstream society, further marginalized them.
However, despite the hardships, Aboriginal communities have shown remarkable resilience. They have fought for recognition of their land rights, their cultural practices, and their right to self-determination.
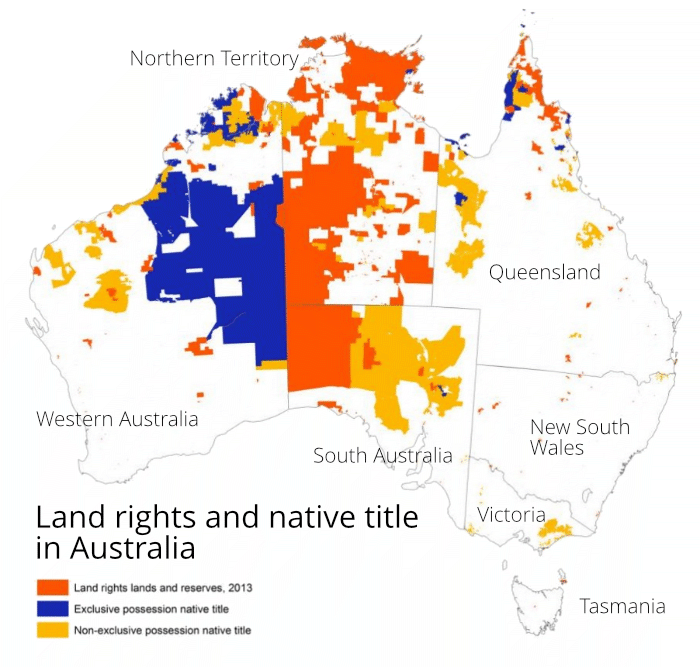
The Map of Aboriginal Reservations: A Mosaic of Cultures

The map of Aboriginal reservations across Australia is a visual representation of the diverse communities and their connection to the land. These reservations vary significantly in size, population, and cultural practices.
- Northern Territory: The Northern Territory is home to the largest number of Aboriginal communities, reflecting the historical and ongoing presence of Aboriginal people in this region.
- Western Australia: The vast landscape of Western Australia is dotted with Aboriginal communities, each with its unique cultural heritage.
- Queensland: Queensland boasts a rich tapestry of Aboriginal cultures, with reservations representing a diverse range of language groups and traditional practices.
- South Australia: The arid landscapes of South Australia are home to numerous Aboriginal communities, many of whom have maintained their traditional ways of life.
- New South Wales: The eastern coast of Australia is also home to a number of Aboriginal communities, with a history intertwined with the development of colonial settlements.
- Victoria: While Victoria has a smaller number of reservations compared to other states, its Aboriginal communities play a vital role in preserving their cultural heritage.
- Tasmania: The island state of Tasmania has a unique history, with its Aboriginal communities facing significant challenges and ongoing struggles for recognition.
Beyond the Map: The Struggle for Self-Determination
The map of Aboriginal reservations is not merely a geographical representation; it’s a symbol of the ongoing fight for self-determination. Aboriginal communities are working to regain control over their lands, their cultures, and their futures.
Key Initiatives and Organizations:
- **The Native

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unmasking the Land: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Australian Aboriginal Reservations. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!



