The Rich Tapestry of Aboriginal Languages: Exploring the Alphabet and Beyond
The Rich Tapestry of Aboriginal Languages: Exploring the Alphabet and Beyond
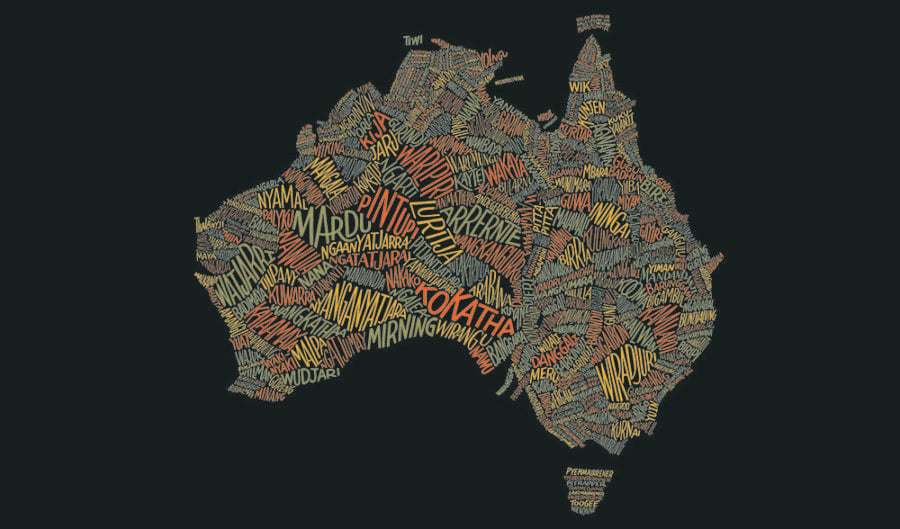
Australia boasts a rich and diverse linguistic landscape, home to over 250 distinct Aboriginal languages. These languages, deeply intertwined with the land and culture of the First Nations people, represent a vibrant legacy spanning millennia. While the exact number of languages is debated, one thing is certain: each language is a unique and complex system, with its own distinct alphabet and grammatical structure.
This article delves into the fascinating world of Aboriginal language alphabets, exploring their origins, diversity, and the challenges they face in the 21st century.
Related Articles: The Rich Tapestry of Aboriginal Languages: Exploring the Alphabet and Beyond
- A Bountiful Harvest: Exploring The Diverse World Of Australian Fruit
- Uncovering The Tapestry Of Sydney’s Indigenous Past: A Journey Through The Clans
- A Guide To Creating A Stunning Australian Native Rock Garden: From Design To Maintenance
- A Tapestry Of Sustainability: How Indigenous Land Management Ensured Economic Survival
- Unraveling The Threads Of Connection: Exploring The Relationship Between Tamil And Australian Tribal Languages
The Origins of Aboriginal Languages:
The origins of Aboriginal languages remain shrouded in mystery, with linguistic experts estimating their existence for tens of thousands of years. These languages predate European colonization and have evolved independently, reflecting the unique cultural and geographical landscapes of Australia.
The Diversity of Aboriginal Alphabets:
Contrary to the misconception that Aboriginal languages use a single alphabet, the reality is far more intricate. Each language boasts its own unique alphabet, often incorporating sounds and symbols not found in the English language.
Key Features of Aboriginal Alphabets:
- Phonetic Representation: Aboriginal alphabets strive to represent the sounds of the language accurately. This means that each letter typically corresponds to a single sound, unlike English where letters can have multiple pronunciations.
- Consonants and Vowels: The number of consonants and vowels varies across languages. Some languages have a rich inventory of consonants, while others have a more limited range. Similarly, the vowel systems can be simple or complex, with some languages having up to seven distinct vowel sounds.
- Diacritics and Special Symbols: Many Aboriginal alphabets utilize diacritics, such as dots, lines, or accents, to modify the pronunciation of letters. This allows for a more precise representation of sounds, particularly in languages with complex tonal systems. Some languages also use special symbols, such as ligatures or glyphs, to represent unique sounds or concepts.

Challenges Facing Aboriginal Languages:
Despite their cultural significance, Aboriginal languages face numerous challenges in the modern era.
- Language Loss: The impact of colonization and assimilation policies has led to a significant decline in the number of speakers of Aboriginal languages. Many languages are considered endangered or critically endangered, with only a handful of fluent speakers remaining.
- Lack of Resources: Limited resources for language revitalization and education have hampered efforts to preserve and promote Aboriginal languages. This includes a shortage of qualified teachers, learning materials, and technological support.
- Social Stigma: In some communities, Aboriginal languages have been stigmatized, leading to a reluctance among younger generations to learn and speak them. This cultural shift has contributed to the decline of language transmission.

Efforts to Revitalize Aboriginal Languages:
Despite the challenges, there is a growing movement to revitalize Aboriginal languages.
- Language Programs: Many communities are implementing language programs in schools, community centers, and online platforms. These programs aim to teach children and adults about their heritage languages and foster language fluency.
- Documentation and Research: Linguists and researchers are working to document and preserve Aboriginal languages through recordings, dictionaries, and grammar books. These resources provide valuable insights into the structure and history of these languages.
- Cultural Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of Aboriginal languages and cultures is crucial for fostering respect and understanding. This includes promoting language learning, celebrating cultural events, and supporting Indigenous-led initiatives.
Examples of Aboriginal Alphabets:
- Yolngu Matha (Northern Territory): This language uses a modified Latin alphabet with diacritics to represent tonal variations.
- Warlpiri (Northern Territory): The Warlpiri alphabet includes a unique symbol for the "ng" sound, which is pronounced like the "ng" in "sing."
- Pitjantjatjara (Western Australia): This language uses a Latin alphabet with diacritics to indicate vowel length and tone.
The Importance of Preserving Aboriginal Languages:
Preserving Aboriginal languages is not just about preserving linguistic diversity; it is about preserving cultural identity and heritage. These languages hold a wealth of knowledge about the land, traditions, and stories of the First Nations people. They are a vital link to the past and a source of inspiration for the future.
Conclusion:
The alphabets of Aboriginal languages represent a rich tapestry of sounds, symbols, and cultural expressions. While facing numerous challenges, these languages are a testament to the resilience and adaptability of the First Nations people. Through continued efforts to revitalize and preserve these languages, we can ensure that the voices of the First Nations people continue to resonate for generations to come.
FAQ about Aboriginal Language Alphabets:
Q: How many Aboriginal languages are there in Australia?
A: The exact number is debated, but estimates range from 250 to 300.
Q: Do all Aboriginal languages use the same alphabet?
A: No, each language has its own unique alphabet.
Q: What are some common features of Aboriginal alphabets?
A: Phonetic representation, unique consonants and vowels, diacritics, and special symbols.
Q: Why are Aboriginal languages facing challenges?
A: Colonization, assimilation policies, lack of resources, and social stigma.
Q: What is being done to revitalize Aboriginal languages?
A: Language programs, documentation, research, and cultural awareness initiatives.
Q: Why is it important to preserve Aboriginal languages?
A: To preserve cultural identity, heritage, and knowledge.
Q: How can I learn more about Aboriginal languages?
A: Explore online resources, visit museums, attend cultural events, and support language learning programs.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Rich Tapestry of Aboriginal Languages: Exploring the Alphabet and Beyond. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!



