A Deep Connection: The Indigenous Relationship with Land and its Importance
A Deep Connection: The Indigenous Relationship with Land and its Importance
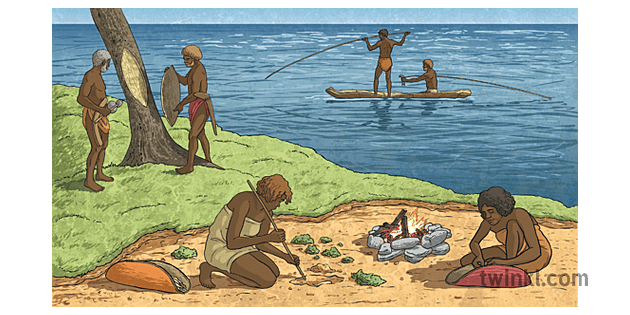
For millennia, Indigenous peoples around the world have held a profound and intricate relationship with their land. This connection goes far beyond mere ownership; it’s a complex tapestry woven from spiritual beliefs, cultural practices, and a deep understanding of the natural world. This article explores the nature of this relationship and its enduring importance, highlighting its significance not just for Indigenous communities but for the planet as a whole.
Beyond Ownership: A Spiritual and Cultural Bond
Related Articles: A Deep Connection: The Indigenous Relationship with Land and its Importance
- Unraveling The Meaning Of "Taurai" In Aboriginal Culture: A Journey Into Language And Spirituality
- Dreamtime And Ancestral Spirits: Unraveling The Tapestry Of Indigenous Australian Culture
- Seeing Beyond The Veil: Unveiling The Power Of Aboriginal Spiritual Seeing
- Unveiling The Mystical Realm Of Narci Indigenous Totem Creatures
- A Journey Through The Realm Of Aboriginal Animals: Unveiling The Spirit Of The Australian Bush
The concept of land ownership, as understood in Western societies, fails to capture the essence of the Indigenous relationship with the earth. For many Indigenous cultures, land is not merely a resource to be exploited but a living entity, a sacred space imbued with ancestral spirits and stories. It is a source of sustenance, identity, and spiritual well-being.
The Land as Ancestor and Teacher:
- Spiritual Connection: Indigenous beliefs often view land as a source of life, a provider of sustenance, and a repository of ancestral spirits. The land is not just a physical entity but a sacred space where generations connect with their past and future.
- Cultural Identity: Land is intimately woven into Indigenous cultures, shaping their languages, traditions, stories, and ceremonies. It provides the context for their social structures, governance systems, and ways of life.
- Knowledge and Stewardship: Indigenous peoples possess a deep understanding of their land’s ecosystems, climate patterns, and natural resources. This knowledge, passed down through generations, enables them to practice sustainable resource management and live in harmony with the environment.
Examples of Indigenous Land Relationships:
- Aboriginal Australians: The concept of "Dreaming" connects Aboriginal people with the land through ancestral beings who shaped the landscape and continue to guide their lives.
- Native American Tribes: Many tribes view land as a sacred gift from their ancestors, and their ceremonies and rituals often involve honoring and respecting the land’s spirits.
- Indigenous Peoples of the Amazon: Their intricate knowledge of the rainforest allows them to utilize its resources sustainably and maintain its ecological balance.

The Importance of Indigenous Land Rights
Recognizing and protecting Indigenous land rights is crucial for a number of reasons:
- Preserving Cultural Heritage: Land is the foundation of Indigenous cultures, and its loss can lead to the erosion of their traditions, languages, and identities.
- Ensuring Environmental Sustainability: Indigenous peoples have a proven track record of sustainable resource management, and their knowledge is essential for protecting biodiversity and mitigating climate change.
- Promoting Social Justice: Recognizing Indigenous land rights is a fundamental step towards addressing historical injustices and promoting equality.
- Supporting Economic Development: Indigenous communities often have innovative and sustainable economic models based on their traditional knowledge and land use practices.

Challenges to Indigenous Land Rights
Despite the growing recognition of the importance of Indigenous land rights, many challenges remain:
- Colonial History: The legacy of colonization has often resulted in the dispossession of Indigenous lands and the suppression of their cultural practices.
- Land Grabbing: Indigenous lands are often targeted for resource extraction, development projects, and other economic activities that threaten their livelihoods and cultural integrity.
- Lack of Recognition: In many countries, Indigenous land rights are not fully recognized or enforced, leaving them vulnerable to exploitation.
Moving Forward: Protecting Indigenous Land Rights
Protecting Indigenous land rights requires a multifaceted approach:
- Legal Recognition: Governments should recognize and enforce Indigenous land rights through legislation and treaties.
- Consultation and Consent: Indigenous communities must be consulted and their consent obtained before any development projects are undertaken on their lands.
- Community Empowerment: Indigenous communities should be empowered to manage their own lands and resources, based on their traditional knowledge and practices.
- International Cooperation: International organizations and governments should work together to support Indigenous land rights and promote sustainable development.
The Future of the Indigenous Relationship with Land
The future of the Indigenous relationship with land depends on the collective efforts of Indigenous communities, governments, and the international community. By recognizing and respecting the deep connection between Indigenous peoples and their land, we can ensure the preservation of their cultural heritage, the protection of the environment, and the creation of a more just and sustainable future for all.
FAQ: The Indigenous Relationship with Land
1. What is the difference between Indigenous land rights and Western concepts of land ownership?
Indigenous land rights are not simply about owning land but about having a deep spiritual, cultural, and historical connection to it. Western concepts of ownership are often based on individual property rights and the right to exploit resources, while Indigenous rights are rooted in a collective responsibility to care for and sustain the land.
2. Why is it important to protect Indigenous land rights?
Protecting Indigenous land rights is essential for preserving their cultural heritage, ensuring environmental sustainability, promoting social justice, and supporting economic development.
3. How can we support Indigenous land rights?
We can support Indigenous land rights by advocating for legal recognition of their rights, promoting consultation and consent, empowering Indigenous communities, and supporting international initiatives that promote their rights.
4. What are some examples of successful Indigenous land management practices?
Indigenous communities around the world have developed innovative and sustainable land management practices, such as rotational grazing, agroforestry, and traditional fishing techniques. These practices demonstrate the importance of Indigenous knowledge and their ability to manage resources sustainably.
5. What are the challenges facing Indigenous land rights today?
Challenges facing Indigenous land rights include the legacy of colonization, land grabbing, lack of recognition, and the impacts of climate change.
Conclusion:
The relationship between Indigenous peoples and their land is a testament to the enduring power of cultural connection, ecological wisdom, and spiritual reverence. By recognizing and protecting this relationship, we can contribute to a more just, sustainable, and harmonious world.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Deep Connection: The Indigenous Relationship with Land and its Importance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!


