The Official Language of Australia: A Deeper Dive into the Linguistic Landscape
The Official Language of Australia: A Deeper Dive into the Linguistic Landscape

Australia, a vast and diverse nation, boasts a rich tapestry of languages spoken across its continent. However, when it comes to official status, there’s only one language that holds the crown: English. This article delves into the fascinating story of how English became the official language of Australia, exploring its historical roots, the diverse linguistic landscape, and the impact of language policies on Australian society.
A Journey Through Time: The Arrival of English
Related Articles: The Official Language of Australia: A Deeper Dive into the Linguistic Landscape
- Uncovering The Rich Tapestry Of Indigenous Cultures: The First Peoples Of Victoria, BC
- Unfurling The Rainbow: The Meaning Behind The Colors Of The Aboriginal Flag
- Unlocking The Heart Of Canada: A Journey Through The Provinces
- A Tapestry Of Cultures: Exploring The Diverse Tribes And Languages Of Western Australia
- Unpacking The Stories Behind Common Aboriginal Surnames: A Journey Through History And Identity
The story of English in Australia begins with the arrival of the First Fleet in 1788. This fleet, carrying over 1,000 convicts and their guards, marked the beginning of European settlement in Australia. The language spoken by these settlers was, unsurprisingly, English, and it quickly became the dominant language in the newly established colonies.
The early years of European settlement were marked by a struggle for survival, with the colonists facing harsh conditions and conflict with the indigenous population. The need for communication and cooperation led to the rapid spread of English, establishing it as the primary language of government, trade, and social interaction.
Indigenous Languages: A Rich Heritage
While English became the dominant language, it’s crucial to acknowledge the rich tapestry of Indigenous languages that existed prior to European arrival. Australia is home to over 250 distinct Indigenous languages, each with its unique history, culture, and traditions. These languages represent a vibrant and ancient heritage that predates the arrival of Europeans by tens of thousands of years.
The impact of colonization, however, has had a devastating effect on Indigenous languages. Many have been lost, with only a handful of speakers remaining. The Australian government has recognized the importance of preserving and revitalizing these languages, and initiatives are underway to support their continued existence.
The Rise of Official Status: A Formal Declaration
The official status of English in Australia was formalized in 1988, with the passing of the Australian Language Act. This act declared English as the official language of the Commonwealth of Australia, recognizing its widespread use in government, education, and public life.
The Act also acknowledges the importance of multilingualism and the right of individuals to use their own languages. It encourages the promotion of Indigenous languages and the support of language diversity in Australia.
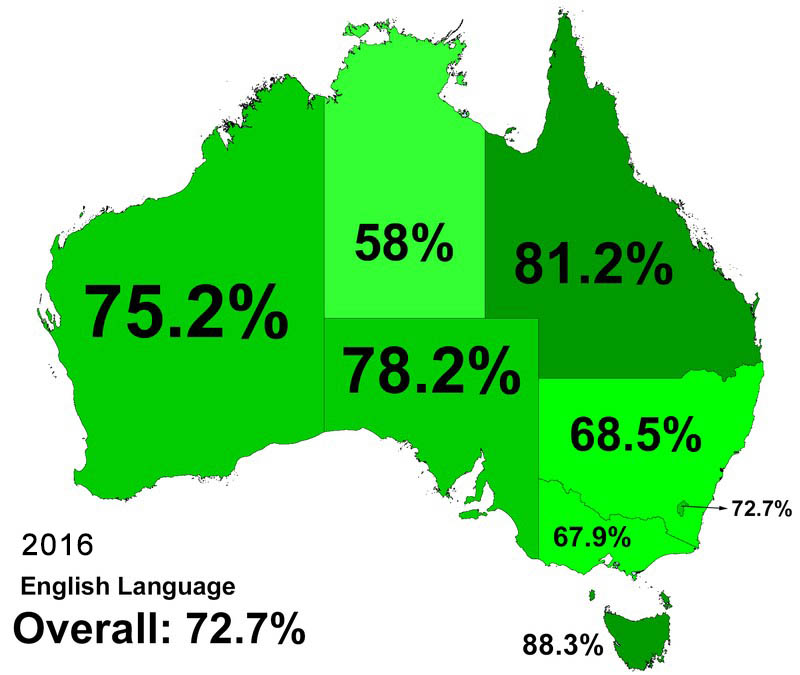
The Linguistic Landscape Today: A Mosaic of Voices
While English remains the dominant language, Australia is a truly multilingual nation. The diverse population, fueled by immigration from all corners of the globe, has enriched the linguistic landscape.
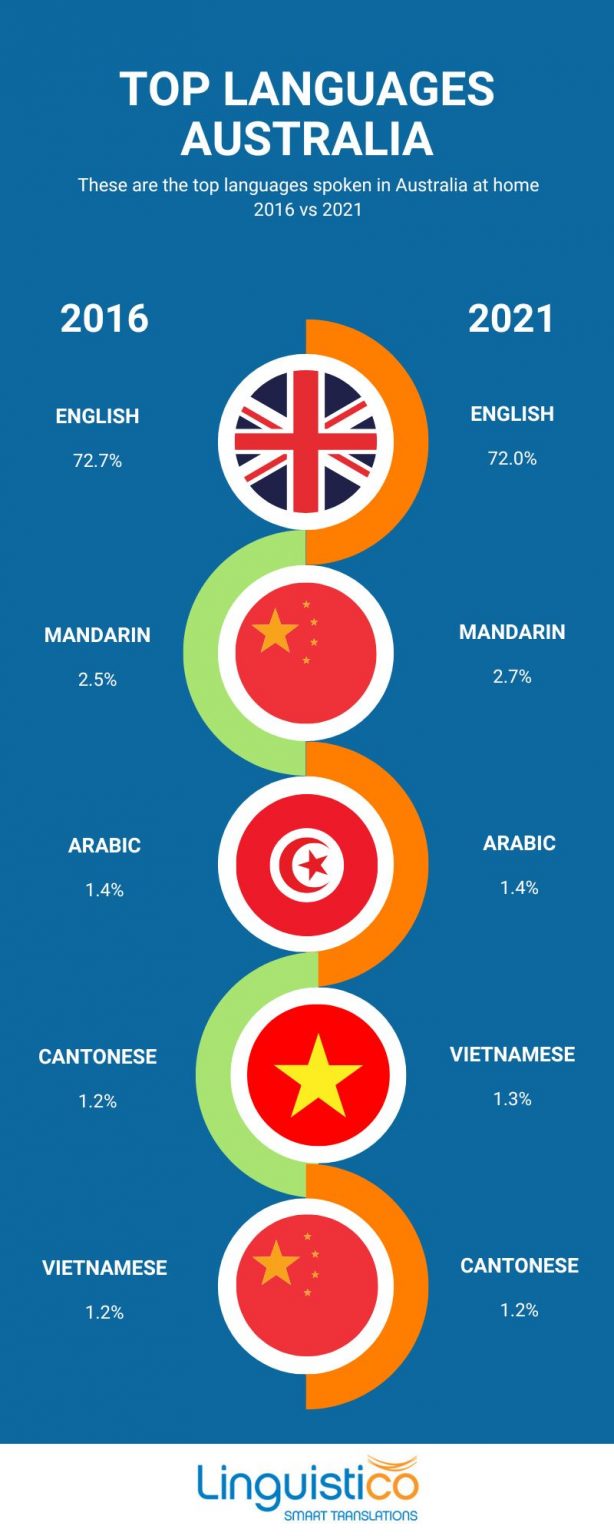
According to the 2016 Census, over 260 languages were spoken at home in Australia. Mandarin, Arabic, Cantonese, Vietnamese, and Italian are among the most commonly spoken languages after English. This linguistic diversity reflects the rich cultural heritage of Australia and contributes to the vibrancy of its society.
The Impact of Language Policies: Balancing Unity and Diversity
The Australian government’s language policies aim to balance the need for national unity with the recognition of linguistic diversity. The official status of English ensures that all Australians have access to information and services, promoting social cohesion and national identity.
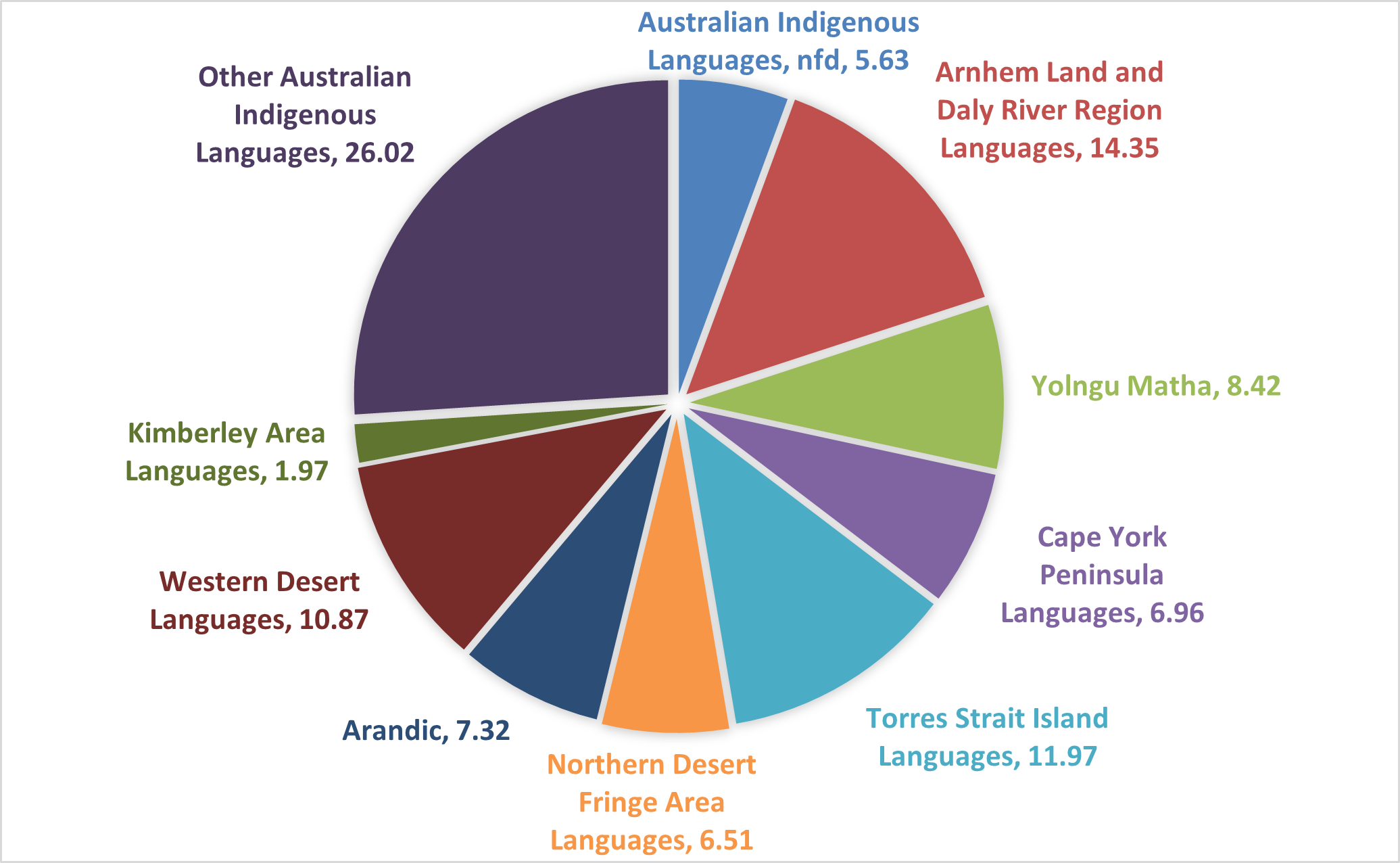
However, the government also acknowledges the importance of supporting and preserving other languages. Initiatives such as language programs, community support services, and the recognition of Indigenous languages contribute to the maintenance of linguistic diversity.
Challenges and Opportunities: Shaping the Future of Language
Despite the official status of English and the government’s efforts to promote multilingualism, challenges remain. The decline of Indigenous languages continues to be a pressing issue, and the integration of newly arrived migrants into Australian society presents its own set of challenges.
However, these challenges also present opportunities. The increasing awareness of the importance of language diversity, coupled with technological advancements, can be leveraged to support the preservation of Indigenous languages and the integration of new arrivals.
Conclusion: A Nation of Many Voices
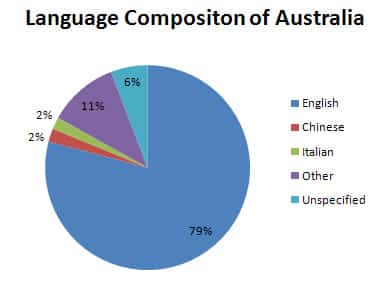
The official language of Australia is English, a language that reflects the country’s colonial history and its role in global affairs. However, the linguistic landscape of Australia is far richer than this single designation suggests. Indigenous languages, languages spoken by migrants, and the evolving nature of English itself all contribute to the vibrant and diverse tapestry of communication in Australia.
As Australia continues to grow and evolve, the language policies of the government will play a crucial role in shaping the future of its linguistic landscape. By balancing the need for national unity with the recognition of linguistic diversity, Australia can create a society that celebrates the richness of its many voices.
FAQ:
Q: Is there any other official language in Australia besides English?
A: No, English is the only official language in Australia. However, the country is home to over 260 languages spoken at home, reflecting its diverse population.
Q: What is the role of the Australian Language Act?
A: The Australian Language Act declared English as the official language of the Commonwealth of Australia. It also acknowledges the importance of multilingualism and the right of individuals to use their own languages.
Q: How is the Australian government supporting Indigenous languages?
A: The government has implemented various initiatives to preserve and revitalize Indigenous languages, including funding for language programs, community support services, and the recognition of Indigenous languages in official settings.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing linguistic diversity in Australia?
A: Challenges include the continued decline of Indigenous languages, the integration of newly arrived migrants into Australian society, and the potential for English to overshadow other languages.
Q: What are some of the opportunities for promoting language diversity in Australia?
A: Opportunities include leveraging technological advancements to support language learning and preservation, promoting multilingualism in education and public life, and celebrating the rich cultural heritage of different language communities.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Official Language of Australia: A Deeper Dive into the Linguistic Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!